Abstract
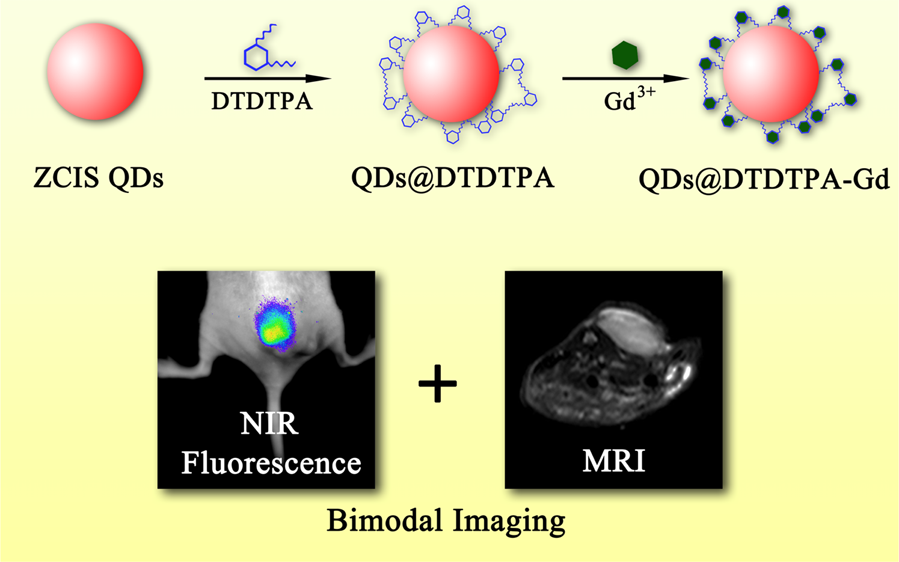
A bimodal contrast nanoagent was developed by chelating gadolinium ions to 2-[bis[2-[carboxymethyl-[2-oxo-2-(2-sulfanylethyl-amino)ethyl]amino]ethyl]amino]acetic acid (DTDTPA)-modified CuInS₂/ZnS quantum dots (QDs). The longitudinal relaxivity (r1) of the resulted QDs@DTDTPA-Gd nanoparticles (NPs) was calculated to be 9.91 mM-¹s-¹, which was 2.5 times as high as that of clinically approved Gd-DTPA (3.9 mM-¹ s-¹). In addition, the in vivo imaging experiments showed that QDs@DTDTPA-Gd NPs could enhance both near-infrared fluorescence and T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) imaging of tumor tissue through passive targeting accumulation. Moreover, the high colloidal and fluorescence stabilities and good biocompatibility indicate that QDs@DTDTPA-Gd NPs have a great potential for use as an efficient nanoagent to integrate the extremely high sensitivity of fluorescence imaging to the high resolution of MR imaging. Integration of bimodal detectability in the same agent of QDs@DTDTPA-Gd NPs can avoid extra stress on the blood clearance mechanisms as the administration of multiple dose of agents.
Authors: Yongbo Yang, Li Lin, Lijia Jing, Xiuli Yue* and Zhifei Dai*
Published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 28 June, 2017
See full text: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021%2Facsami.7b05867